Modern LED lamps can be classified according to several features:
by the purpose of the lamp;
by the type of its construction;
by type of cap;
by the properties of the emitted light.
By appointment, LED lamps are divided into:
main lighting lamps in living areas;
lamps for local design highlights;
lamps for external architectural lighting and landscape design;
lamps for use in an explosive atmosphere;
lamps for street lighting, car parks, bridges, sidewalks, railway stations, etc .;
lamps for searchlights, which are installed on industrial buildings and territories.

According to the type, depending on other properties, the LED lamps are divided into:
general purpose lamps for residential and office premises;
lamps of directional light for projectors that are applicable both for local illumination of the interiors of buildings, shop windows, advertising constructions, and for landscape lighting;
linear lamps in the form of oblong tubes, to replace fluorescent lamps.
By the type of socle, there are mainly five main types:

Plinths E27, E14
Standard threaded connection, found in the most ordinary incandescent lamps. This type of socle was introduced by Edison himself, and the letter "E" is the first letter of the inventor's surname. The numbers indicate the diameter of the cap in millimeters.
Today, the socles E27, E14 and other sizes, are the most common types among all socles, including among LED lamps. The E14 cap is also called the "minion". Lamps with such a cap usually have a flask in the shape of a candle, an elongated shape, and are used mainly in sconces, in floor lamps, and in table lamps.

Two-pin connector, the pins of which have thickenings at the ends, designed to rotate the lamp in the chuck. Such socles have, for example, starters in old gas-discharge lamps widely used before in public places. The letters in the name of the socle designate the following: G - pin base, U - with thickenings at the ends. 10mm is the distance between the pins.
This type of socle is the most electrically safe, it is convenient to use, and LED lamps with such a base are usually designed for 220 volts. Mainly, the lamps with such a base are those that are installed in the ceiling lamps (reflex LED lamps).

The plinths of type GU5.3, the caps of the same pin family, have become widespread recently, when halogen reflective lamps in ceiling luminaires have become widespread. Basically, this is spot lighting, mounted in plasterboard ceilings.
LED lamps with the same base, came to replace the same base, and easily mounted in cartridges. Holes in the cartridges under this base, exactly match, the distance between the pins exactly the same as the holes, and is 5.3 mm, so the installation is fairly simple and safe.

This socle is characteristic of linear tubes in the form of tubes. As in the previous case, 13 is the distance between the pins in millimeters. Often, these are lamps for ceiling luminaires, which are often used for lighting large areas of shopping centers, warehouses, production halls, and other rooms where the ceiling is high enough and the area is long.

As for the marking of LED lamps, it is similar to the marking of compact fluorescent lamps (CFL), and on the packaging the manufacturer indicates exhaustive information about the product. In addition to the inscription LED, which indicates that the lamp is LED, other lamp parameters are also reported. Let's consider in more detail, on an example that is specified on packing, and what there are these parameters.

Power
The packaging must indicate the power consumed by this LED lamp from the network. As a rule, the packaging indicates the equivalent of the light flux of incandescent lamps, but this equivalent parameter is given only for comparison. The real one, which is currently available for sale, is in the range of 1 to 25 W, depending on the needs of the buyer.
Comparison of LED lamps with other types of lamps:
Life time
Service life in hours. This parameter varies from manufacturer to manufacturer, and according to statistics, the service life of LED lamps in normal, not extreme conditions, with high-quality power from the network can reach 50,000 hours.

Energy efficiency class
Of course, LED lamps are very energy efficient, and the packaging is always indicated. If earlier this indicator was limited to level "A", then with the development of energy-efficient LED lighting, there were additional classes "A +" and "A ++", indicating a significantly lower value of the ratio of power consumption to power, calculated from the effective lamp received from this lamp light flux.

Type of bulb
In this example, the type of the A55 flask is a standard shape, as in a conventional incandescent lamp. There are other options: C35 - candle, G45 - ball, R39, R50, R63 - mirror, and others. The bulb can be matt or transparent, this is indicated on the package.

It can be different, from very warm to very cold, and for a person more comfortable is a "warm" light, closer to the yellow, as is the case with incandescent lamps. Cold light is more suitable for industrial premises, street lighting and other places where a person does not seek maximum comfort, and if a cold light is installed in a residential building, it will be unfair to affect the human nervous system. On the package, this figure must be indicated.
The color temperature is measured in Kelvin, and the ranges have corresponding names when labeled: warm white light (2700-3200 K), neutral white or daylight (3500-4500 K), white light (4700-6000 K), cold white light (from 6000 K).
The indicator of the brightness of the LED lamp, measured in Lumens. For clarity, you can use the table, and get an idea of the light flux that conventional incandescent lamps give. Of course, LED lamps are able to give the corresponding luminous flux, consuming 7-10 times less electrical energy.

Color rendering index Ra
For sunlight, this is 100, for incandescent lamps - from 90 and above, for LED - from 80 to 89. This indicator reflects how close to its natural color, the body illuminated by this light source remains. Ra is more than 80 is generally considered high enough.
Consumption parameters
In the above example, it can be seen that this LED lamp can operate at a temperature of -40 to +40 degrees Celsius, supply alternating voltage from 150 to 250 V, frequency 50/60 Hz, with the maximum (peak) current consumption will be 0.065 A .
In recent years, the development of LED technology has reached a level where energy-saving LED light sources have become more affordable and gradually supplant other lighting devices from the market. All types of LED lamps, regardless of their specific application, are characterized by a long service life (up to 100,000 hours), low power consumption (2-8 times less than conventional artificial lighting devices), environmental friendliness, and safety of operation and recycling.
Classification of Led-lamps
Depending on the application, there are several main types of LED lamps:
- Led-lamps for general lighting of residential interiors and offices.
- LED lamps for interior lighting.
- LEDs for architectural outdoor lighting of buildings and landscape design.
- Explosion-proof LED lamps are designed for use in explosive atmospheres.
- Street LED lights - used for lighting roads, bridges, pedestrian crossings, railway stations, entrances and parking areas. Led-lamps for street lighting have anti-vandal protection, are able to work under all weather conditions, including sudden temperature fluctuations.
- Industrial LED spotlights are powerful lamps designed to illuminate large production areas and squares.
According to the type of housing design and the properties of the emitted light flux, LED bulbs come in three varieties:
- led lamps of general purpose - are a source of pleasant for the eyes, quality scattered light, as close to natural daylight, designed for indoor lighting of residential facilities and office space;
- led-directional light lamps - used for highlighting trade, exhibition and antique shop windows, in accent interior lighting;
- linear LED lamps - are made in the form of an elongated tube with a rotating base. The design of the device allows you to easily change the angle of light of the lamp. In general, bulb-tubes are used for office lighting.
Video review of the classification of LED lamps
Varieties of LED lamps by cap type
1. The base of Edison (E)
Lamp with threaded connection system to power supply. This is the very first and most common form of the plinth design. The figure indicated in the marking after the letter E is the diameter of the threaded connection, for example, a lamp of the standard size E27 and E14 (minion). These LED lamps are designed to work in a network with a voltage of 220 V and do not require the connection of special devices - adapters.
2. The pin socket (G)
Cap G - pin system connecting the lamp with the cartridge. Fastening plugs are usually a pair of contacts of the specified length and thickness, and also can be made in the form of a loop of wire. The number in the marking indicates the distance (mm) between the center of the pins or the diameter of the cap of the cap, if the lamp has more than 2 connecting devices. Lowercase letters in the marking indicate the number of pins: 1 contact - s, 2 contacts - d, 3 contacts - t, 4 contacts - q and 5 pins - p. Lamps with a bayonet mount base are available in low-voltage or standard, designed for operation in 220V networks. In the first case, when connecting the device to the power grid, a special voltage adapter is required.
3. Bulb lamps - (T)
LED tube lamps are produced with a rotating base in several sizes: 5/8 inch / 15.9 mm - T5, 8/8 inch / 25.4 mm lamps - T8, 10/8 inch / 31.7 mm - T10 and 12/8 inch / 38.0 mm - T12 lamps.
LED lamps are also available with other types of socles, but they are less common: a socket with a recessed contact (R) focusing (P), a soffit (S) and a pin socket (B).
LED lighting is the most perfect type of lighting at the moment. The principle of operation of LED lamps is based on the fact that when passing through a semiconductor a certain type of electric toga light is emitted. Let's not go into the physical details of why this happens. I will say just that this effect was discovered in the early twentieth century in Britain and for a long time it was not used.
The active use of LEDs began in the 50-70s of the last century. The first LEDs emitted a very dim light and as a rule it was red. Such diodes were used mainly as indicators for various measuring instruments. A wide application of LEDs began only when a bright blue LED was obtained in the Nichia laboratory in 1990. LED lamps consist not only of the diodes themselves. They also include a lens that dissipates the light flux. The lens is coated with a ball of a special dye - phosphor. With the help of this ball you can get white light or a warmer temperature - yellow.
More on the history of the creation and distribution of LED lamps, we'll talk in the next article, and in this let's look at what they are. In fact, there are so many types of LED lighting lamps. It depends on their purpose, manufacturing technology, capabilities and other parameters. In this article, we will try to disassemble all types of LED lamps. So that when you decide to replace the usual lamps with LEDs, you know all that you can about what they are.
First, let's look at the most common classification. This is a classification by field of application. It is a bit blurry, because the boundaries between the categories are set not so much by the peculiarities of the lamps themselves, so much where you will apply them.
And so, for the field of application we will distinguish such kinds of LED lighting lamps:
- Street - these lamps are used to illuminate various objects on the street: houses, roads, parks. They are distinguished by high resistance to weather conditions and mechanical damage. Can not be suitable for use in the house because of the non-standard size of the socle and as a rule very bright.
- Lamps for home - The purpose of these lamps is to replace conventional incandescent lamps, they usually correspond to them in size, shape, appearance. Also they have a standard size of the cap, the same as in conventional lamps and the parameters of the light flux are not very different.
- Searchlights - specially designed lamps with the required brightness of light, directivity and dispersion angle suitable for use in projectors.
- Industrial lamps - used for lighting hangars, warehouses, garages and other large industrial premises. They are characterized by high brightness, scattering angle, and protection against damage.
- LED Bulbs for Plants - these lamps are specially designed to improve the growth of plants. The color and spectrum of the radiation are correctly selected, and they are also capable of emitting ultraviolet radiation. Usually they are smart lamps. What is a smart lamp, we'll talk below.
- Car Lights - lamps intended for use in cars: interior lighting, in driving and driving lights.
- Decorative lamps - these lamps do not set a goal to illuminate the room, but rather decorate it. They can be of various colors, and also, as a rule, have a small angle of dispersion.
If you look closely, on our website for each type of LED lamps there is a section where in the future their features and proper use will be described in detail. The main classification was considered, so to speak, to create a foundation, now let's look at the types of lamps depending on their structure and functions.
LED lamps can use a different type of LED matrix. Here are the types of construction of LED lamps:
- Usual LED matrix - on the matrix are placed the usual blue LEDs, and the lens is coated with a ball of a special substance - a phosphor that converts the blue light, and we get a white or yellow shade that we need.
- RGB Matrix - Such a matrix contains three different types of diodes - red, green and blue. Accordingly, Red, Green and Blue. When we mix these colors, we get also white. Here in the lamp it is possible to fine-tune the shade of color by adding or decreasing the intensity of one or another type of diodes. But in this way, much less energy efficiency.
Also in different lamps can be used, the LEDs are manufactured using different technologies. LEDs are:
- DIP and Superflux - these very popular LEDs are used in various devices, indicators and displays, but they give a very low luminous flux, therefore, for use in LED lamps are not suitable.
- SMD(Surface Mounted Device) - the most popular LEDs used in LED lamps. As the name implies, they are fixed to the board surface. The LEDs SMD xxxx are designated, where xxxx is four digits, meaning the board size in millimeters. They can be used not only in LED lamps, but anywhere and deserve their popularity with ease of installation, use and low power consumption. For example a diode SMD5730 measuring 5.7 by 3 mm consumes 0.5 watts and emits 55 lumens of light.
- Powerful SMD LEDs - specially designed for use in lighting. Usually consume about 10 watts and more energy, shine very brightly and do not require additional lenses to disperse the light.
- COB (Chip on Board) is the most modern type of LEDs. The diode chip is fixed directly to the board, and this improves such characteristics as cooling, reduces the volume and makes the light more uniform.
If the used LEDs and the type of matrix for you are not very important, then the size of the cap, this is something you will come across for sure. So here you need a little knowledge not to buy a light bulb which will not know where to screw it. The most common types of socks for LED lighting lamps are:
- E27 - the most common socket with a thread oriented to use instead of conventional incandescent lamps. You can say this is the standard type of socle of LED lamps for the home. \\
- E14 - a reduced version of the socle E27. Suitable lamps are mainly for modern lamps and chandeliers.
- E40 - very large base with thread. Such lamps are used in industry.
- GU5.3 - a relatively new type of socle, is designed to replace halogen lamps with LED. It consists of two small pins, exactly the same as in halogen lamps. When replacing the cartridge and cap are fully compatible and no rework is required.
- GU10 - one more socle of type GU, is most often used in pendant lighting fixtures.
- G13 - The type of socle with two pins, is used most often in ceiling light fixtures.
- G4 - the plinth consisting of two small wires at the end, is used as a rule in small bulbs.
- G9 - another base designed to replace halogen lamps.
- R7s - the plinth of quartz lamps of searchlights.
- G23 - socle of compact fluorescent lamps.
Another LED lamp can be divided by the heat of the light emitted by them. Conventional incandescent lamps can only emit a yellow color. At the same time, several shades are available:
- very cold blue
- natural white
- warm shade of white
- yellow shade
- pinkish shade, it looks like it before dawn
In general, the temperature of LED lamps can vary from 2600 to 6000 degrees Kelvin.
Due to the power supply in the lamp housing, the LED lamps can work from different voltages and types of current. The most common of them are:
- 220 V - alternating voltage of the network we are familiar with
- 12 V - constant pressure. Used most often in cars and other lamps working on batteries.
- 9 V - also a constant voltage, one more variant of light-emitting diode lamps for cars.
Depending on the additional features, these types of LED lighting lamps are distinguished:
- dimerable - these lamps maintain the brightness adjustment with the help of conventional dimers. In the lamp housing, there is a special device that perceives the change of current and correctly interprets this change by lowering or increasing the brightness of the LEDs. Such lamps are much more expensive than conventional ones and they are more difficult to find.
- smart lamps - these lamps, in addition to their main function - to shine, can be controlled via Bluetooth using a smartphone or tablet, programmed to turn on or off at a given time and many other actions. They cost even more than dimmable lamps.
The last thing I would like to consider in the article about the types of LED lighting lamps is the shape and size of the lamps. This is a very extensive topic, since there are a lot of forms of LED lamps and pictures are indispensable here. But we will discuss it in detail in the next article, but for now we just list the names:
- Pear
- Candle
- Ellipse
- A tube
- Reflector
- Corn
conclusions
In this article, we examined the general concepts of the classification of LED lamps. A more detailed description on some broad topics, such as the type of socle and the shape of the lamp, can be found in the following articles. If you have any questions or suggestions for improving the article - write in the comments!
If you find an error, please select the text fragment with an error and click Ctrl + Enter.
Post Views: 4,389
LED lamps or LED lamps (LED - Light Emitting Diodes) - these are modern energy-saving light sources designed for street lighting, industrial, public, residential and other facilities.
How to choose the right LED bulb (LED lamp)?
The principle of operation of LED lamps is based on a physical phenomenon electroluminescence , when an electric current passes through two conductors located at a certain distance from each other, electromagnetic radiation of the visible spectrum is emitted, which is light.
Types of LED lamps
LED lamps are classified according to the following features:
- on the field of application;
- by type of LED;
- by type of cap.
LED lamps differ depending on the type and size of the cap:
- The base of "Edison" , a threaded connection, which is indicated by the letter "E". The figures after the letter in the cap marking mean its diameter (mm). For example:
- E27 - LED lamp, threaded connection, cap diameter 27 mm;
- E14 - LED lamp, the connection is threaded, the diameter of the cap is 14 mm.
- Cap with pin connection is denoted by the letter "G". The second letter denotes certain features in the design of the pin. The digits after the letter indicate the distance between the pins (pins) in mm. For example:
- MR16 - LED lamp with a reflector (similar in shape to halogen lamps), which come with a socket size GU 5.3 or G5.3;
- G4 - LED lamp, pins connection, distance between contact pads 4 mm;
- GU10 - LED lamp, pin connection, usually used for lighting pictures, various elements of the room, as well as for highlighting the interior of the room as a whole, the distance between the contacts is 10 mm.
- Socket with recessed contact, is denoted by the letter "R". The figure after the letter indicates the depth of the contacts relative to the surface of the base (in mm).
Types and designation of plinths of LED lamps, photo 1.
Depending on the application, LED lamps are divided into:
- lamps of external illumination (outdoor) - for lighting streets, parks, lawns, building facades. These lamps are equipped with increased protection from the environment and mechanical influences, photo 2a;
- industrial lamps , including searchlight - for lighting of industrial premises, workshops and territorial sections of enterprises, photo 2b.These lamps have a high power (up to 1 kW) and an indicator of light efficiency;
- lamps for household use - for lighting of living quarters and offices, photo 2в.
- car lamps .
Photo 1. Varieties of socks of LED lamps

Photo 2. Types of LED lamps, depending on the purpose: a) external lighting lamps (outdoor); b) production lamps; c) household lamps
By type of device, the LEDs are divided into:
- SMD ( Surface Mounted Device ) - the most common LEDs, photo 3. In the designation of the LEDs, the type (abbreviation in letters) and the LED size in mm (4 digits) are indicated. The most common LEDs are SMD: SMD3528 - diode 35 × 28 mm; SMD5050 - a diode of 50 × 50 mm.

Photo 3. SMD LEDs: SMD3528 (left) and SMD5050 (right)
- COB ( Chip on Board ) - a new generation of LEDs with an improved LED structure, has greater light output, photo 4.

Photo 4. COB LEDs
- high power LEDs are designed for industrial lighting, photo 5. The current consumption of such lamps can be 1 ... 10 A and more (type 5630, 5730) and power up to 1 kW.

Photo 5. High power LEDs
The LED lamp consists of such components, photo 6:
- diffuser plastic - this is the upper part of the construction of a special plastic, which evenly disperses the light rays of the lamp;
- lED or LED module (with a large number of LEDs) - a light source. The number of LEDs in a single lamp can reach several dozen. LEDs are mounted on an aluminum mounting plate;
- aluminum printed circuit board (thermal conductive platform), which is designed to remove heat from the chips to the radiator providing the required temperature level for the normal operation of the LEDs. The printed circuit board is installed on the thermal paste (special with increased thermal conductivity of the paste);
- aluminum radiator - designed to remove the temperature from the diodes. Normal operation of the radiator is a guarantee of the durability of the lamp and in particular of the LEDs;
- IC driver (converter) - A special electrical element that converts and aligns the alternating current into a constant one. The driver can extend the life of the lamp. The power factor of the driver IC (power supply) must be at least 0.9. A good quality driver has protection against power surges, breakdowns and overheating.
- socle – allows you to establish a reliable contact with the device of the lamp and the source of electricity.

Photo 6. The device of the LED lamp
Advantages of LED lamps
- Low power consumption (10 and more times less than the consumption of electricity in traditional incandescent lamps).
- Long service life (within 20 000 ... 100 000 hours, this roughly corresponds to 10 ... 40 years of operation). Traditionally, the manufacturers of lamps give a guarantee - 2 ... 3 years.
- Low heat dissipation, compared to incandescent lamps. In this regard, the plinths of chandeliers and lamps, which are now increasingly made of heat-resistant plastics have a much greater service life (when using incandescent lamps, the plinths tend to quickly become brittle and are destroyed by prolonged temperature effects).
- Resistance to mechanical influences.
- Environmentally friendly view of lamps. Does not contain or emit fumes of mercury and other substances harmful to human health. No need for special disposal of lamps.
- Wide temperature range of the lamps: -40 ... + 60 ° С.
- Frequent switching on and switching off the lamp does not affect its durability.
- Instant heating of the lamp (almost immediately).
- In the light flux of LED lamps there is no ultraviolet radiation.
- High luminous efficiency (more than 5 ... 8 times from a normal lamp) - 1 W produces 70 lumens (lumens), photo 7.
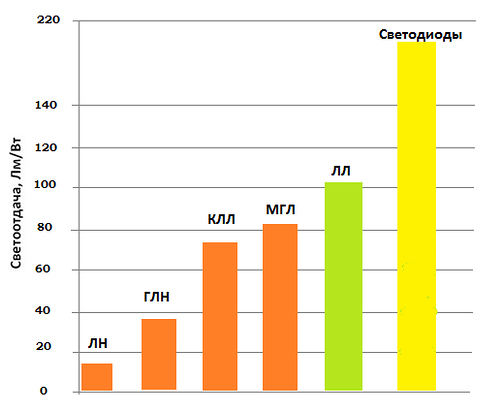
Photo 7. Comparative diagram of light output of different types of lamps
- Ability to choose the color of visible lamp radiation (color temperature of the LED), photo 8. Can choose:
- warm white light, corresponds to the light from a conventional incandescent lamp (2700 ... 3000 K);
- natural white light (imitation of daylight) - 4000 ... 4400 K;
- cold white light - 6000 ... 6500 K, photo 8а;
- any color and shade (for decorative lighting), photo 8b.
- Ability to adjust the brightness of the LEDs.

Photo 8. Selecting the color temperature of the LED: a) color temperature scale; b) options for decorative lighting
Disadvantages of LED lamps
- High cost (payback of the LED lamp is 3 ... 5 years).
- In cheap lamps, by using cheap elements, in particular capacitors, high-frequency flicker of light can occur. Such flicker can irritate the human retina and lead to eye disease (according to the research of Spanish scientists).
- With poor quality of heat sink, the durability of cheap LED lamps is low.
- The LED shines in almost the same direction, the illumination angle is up to 120 °.
- Over time, the light from the LEDs fade, which is especially true for low quality lamps. The rate of decrease in the intensity of the light flux depends on the quality of the heat sink.
Below are the comparative parameters of various types of lamps, photo 9.

Photo 9. Comparative parameters of different types of lamps
Tips for choosing a LED lamp for lighting a living room
When choosing LED lamps (LED lamps) of optimum quality and performance, you should pay attention to the following parameters:
- Parameters of light efficiency. The parameter of light efficiency should be not less than 100 Lm / W. Often this parameter is not written on the lamp or the box, then it can be determined by a simple calculation: the illumination (Lm (lumen)) should be divided by the lamp power, which is indicated in watts (W).
- Colorful temperature. The value of the color temperature, which is optimal for perception by the human eye and should be 4000 K. Also an optimal solution for children's rooms and lighting in the evening will be lamps with a color temperature close to 3500 K ("soft white light) photo 9.
- Lamp power. By power also indirectly one can judge the light efficiency of a lamp. There are tables on which it is possible to determine the correspondence between the power of the LED lamp and the piercing lamp, photo 10,and, based on this, determine what power it is to buy an LED lamp. Usually, the light efficiency of LED lamps is 8 ... 10 times higher than the incandescent lamps.

Photo 10. Comparative tables of light efficiency on the power of an LED lamp and other types of lamps
- Verify the efficiency of the heat sink. As mentioned above, good quality LED lamps are equipped with a heat sink, the design of which is made in this way (the presence of ribs and spirals), so as to maximize heat. It is approximately possible to determine the quality of the heat sink according to the heating temperature of the housing after a short time after switching on the lamp. Also, the quality control of the lamp and its heat sink can be determined with the help of a special instrument - luxmeter. If the luxmeter captures a decrease in the lamp's light intensity by more than 10% after 40 minutes after switching on - then this lamp is not of high quality and is equipped with a cheap and inefficient heat sink. Low-quality lamps have a low indicator of light efficiency and durability. If there is no heat sink in the form of a radiator (if the lamp power is more than 4 ... 10 W or more), do not buy LED lamps.
- Check for pulsation. Quality LED lamps have a low pulsation coefficient of the light flux. Check the degree of ripple can be using an ordinary mobile phone - when you point the phone's video camera on the screen should not appear stripes and flicker.
- Manufacturer. High quality LED lamps are manufactured by such manufacturers as Osram (Germany), CREE (USA), Philips, Seoul Semiconductors (Korea), Nichia. There are also other manufacturers who produce high-quality products, but one should refrain from buying cheap lamps, especially Chinese ones.
Low-quality LED lamps use sapphire as part of the LED, which is not a reliable material. The manufacturers of high-quality products in the manufacture of light-emitting diodes use silicon carbide.
Guided by these tips, you can buy the optimum quality of the lamp, which for many years will effectively illuminate your production, houses, offices and suburban areas.
You can further save energy by applying motion sensors.
The publication was prepared by an expert
Konev Alexander Anatolievich
