An electrical wire, cable or cord is a copper or aluminum conductor through which current flows and insulation that protects the line from short circuit, and a person from exposure to dangerous voltage. All kinds of wires differ only in the thickness of the metal strands and in the insulation material, which determines its resistance to heat, the environment and probability of ignition.
Main types of wires
First of all, the division is made according to the purpose. The very first species electrical wires and the cables were power, intended to deliver electricity to the consumer. Then it turned out that alternating current it is more profitable to use for electricity transmission and the higher the voltage, the less loss, so the search for its optimal values began. As a result - power wires are divided by those that transmit electricity from power plants to cities (with a voltage of 20-150 thousand volts) and such that directly bring it to consumers' homes (110-380 Volts).

With the invention and the development of telephone communications, the corresponding wires have appeared - since telephones do not need a lot of voltage for work, then it is too expensive to use power wiring for them. In addition, to connect a large number of subscribers needed cables with an appropriate number of cores and protection against moisture ingress.


When it became necessary to connect computers to a single network, new types of cables and wires were needed - specifically for these purposes. Initially, telephone lines were used for these purposes, but the data transfer rate remained at a very low level. A breakthrough in this area came with the invention of optical fiber, which was used to transmit the signal over long distances. To connect local local networks, twisted-pair cables began to be used.
In addition to the basic types of wires used non-standard - for example, for heating, lighting or simply decorative.
Power wires
Are intended for transfer of the electric power from power stations up to distributive transformers and further to the end user. In the first case, wires are used that are designed to operate in the open air and withstand a voltage of up to 150 kVolt - the optimum value for long-distance transmission of electricity.
Household power wiring is designed alternating current frequency of 50-60 Hertz and voltage up to 1000 volts. Often a classification is used for the material of current-carrying veins, which can be made of aluminum, its alloys or copper. Aluminum is cheaper in production, while copper has less resistance to electric current, so they have a smaller cross section. It is more preferable to use copper wire - it is durable and reliable, but because of the price, aluminum is still used quite often, and in power lines and in general - almost everywhere.
VVG is the market leader
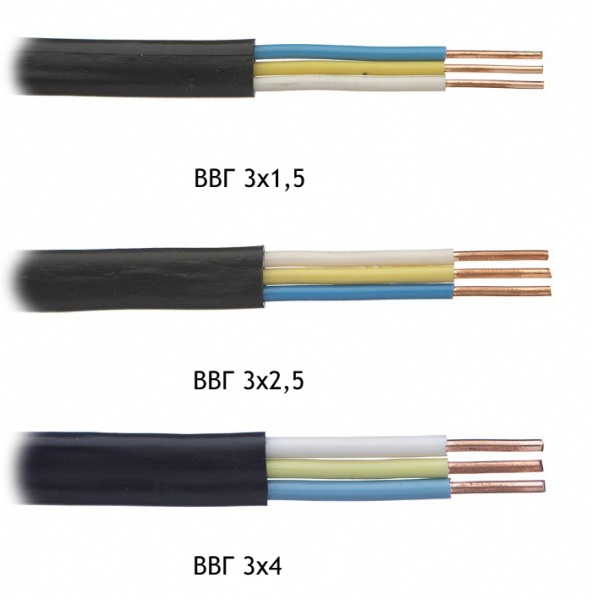

Cable for laying electrical networks with double PVC insulation - multi-colored on each vein and common cambric. Current-carrying veins are single or multiwire, with a cross section of 1.5-240 mm². Has such varieties:
- AVVG. The letter "A" before the title says that the cores of the cable are made of aluminum.
- VVGng. Wire insulation does not ignite over a larger temperature range.
- VVGp. It differs only in appearance - a flat form.
- VVGz. A cable of increased security - inside it all empty spaces are filled with a rubber compound.
NYM Cable
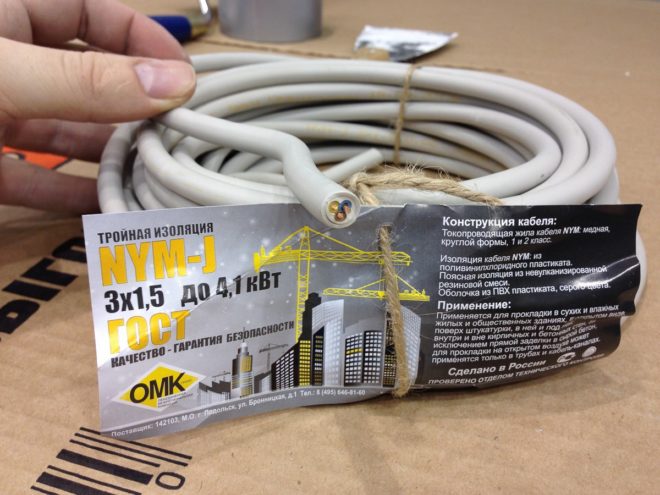

It is made according to European standards and although similar in current-conducting properties to VVG wires, it is superior to domestic analogues in insulation class, as during manufacture, voids between the cores are filled with coated rubber. It is made with the number of current-carrying veins from 2 to 5, section 1,5-16 mm². Outdoor installation is permitted, but with additional protection from sunlight, since the insulation is not resistant to ultraviolet light. Unlike domestic analogues it can be laid with a radius of bending from 4 of its diameters.
KG - flexible cable

Without loss of its properties, the cable can be operated at temperatures from -60 to +50 ° C. It is most often used to connect electrical appliances to a network, and its cores are designed for a current frequency of up to 400 Hz, which makes it a good choice for use in welding machines. Current-carrying conductors are only copper stranded with rubber insulation. The number can be from 1 to 6, hidden under a common outer shell.
VBBShv - armored
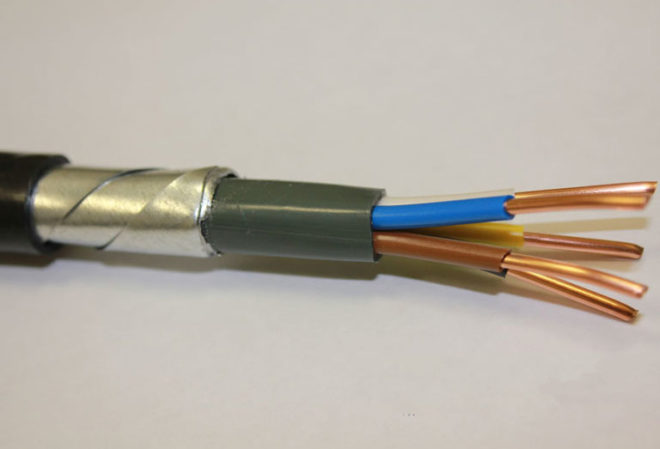
Increased protection against mechanical damage is ensured by belts, with which the wires are wrapped before applying the main insulation layer. Current-carrying veins made of copper, separately insulated PVC, quantity - 1-5 pieces, consisting of one or more wires. Single-core cables are used for DC transmission.
To use the cable there is one limitation - installation is recommended without UV protection. Its following types are applied:
- AVBBShv - with veins from aluminum;
- VBBShvng - with excessive heating, insulation does not burn, but smoldering;
- VBBShvng-LS is the minimum of smoke and gases in decay.
Cables for telephone lines
There are two kinds of wires and electrical cables - to connect to the line switchboard and to it already to connect separate subscribers.

Antenna Cables

Despite the simplicity, these cables have many characteristics, for which they must be selected:
For more information on selecting an antenna cable, see this video:
Computer Cables
By analogy with telephones, two main types of wires are used here - for connecting end users with a switchgear and connecting the latter with the world wide web.

An optical fiber used to transmit data over long distances is not an electrical cable, since it does not electricity, but light pulses that still need to be converted into electrical ones. To connect such wires you need special equipment and highly skilled personnel, so in everyday life they are practically not used.

Twisted pair. The wire, well known to Internet users - it is this cable that comes to the computer and connects to its network card. Structurally represents eight current-carrying strands twisted together in pairs. Each vein has a separate PVC or propylene insulation and, depending on the classification of the wire, all of them can be covered with additional protective and screening layers:
- UTP - all wires are twisted in pairs, and from above are closed only by the outer shell;
- FTP - under the outer shell there is a screen made of a layer of foil;
- STP - cable with double shielding. A separate screen is on each twisted pair and all together is surrounded by a braid of copper wire;
- S / FTP is also a double shielding, only here is a screen made of foil.
Special Purpose Wires
Use the same kinds of electrical wires if they require special properties that are not available for conventional cables and for connecting electrical equipment in places where the use of standard conductors is difficult or impossible at all. For example, conventional wires can not be used when connecting electric ovens, which are heated to high temperatures. The same applies to bathhouses or cellars, where, apart from the temperature, the humidity factor must be taken into account.
In addition to exposure to temperature and moisture, the probability of mechanical damage should be considered, especially for wires that are laid underground.
Non-standard power wires

RCMM. Flexible solid conductor for installation of power wiring in places with high temperature - does not change its characteristics in the range from -60 to +180 C °. The insulation material withstands a voltage of up to 660 volts, is resistant to vibration, 100% humidity of the air, does not deteriorate from exposure to mold and contact with aggressive liquids - varnishes or solvents.

PNSV. Single-core steel wire in PVC insulation with conductor section from 1.2 to 3 mm². The material and the cross section are selected in such a way that the wire heats up when an electric current passes through itself. Most often it is used as a heating element in warm floors or on construction sites when pouring concrete in the cold season - this allows the use of concrete solutions at minus temperatures.

Runway. Multi-wire single-core wire, cross-section from 1.2 to 25 mm² with double insulation. Designed to work in artesian wells, where it is used to connect power to the motors of electric pumps - i.e. not afraid of water and high pressure.
Non-standard decorative wiring

LED cable. In addition to the main conductors, there is an additional circuit, to which LEDs are connected. They are located under a transparent outer shell at a distance of about 2 cm from each other and begin to glow when the wire is connected to the network. The connection scheme of LEDs is series-parallel, which allows to cut the wire in any place, and also, in case of damage, shows the place of cable breakage. If you select wires with different colors of LEDs, you can create whole pictures, which determines the most demanded niche of using such a cable - the stage effects and the connection of the equipment necessary for them.

Electroluminescent wires - work thanks to the phenomenon of pre-breakdown electroluminescence of solids. The main core of the wire is covered with a phosphor and a dielectric layer. From above it is wrapped by two thin wires and everything is applied to dielectric - transparent or colored. In fact, the main core and additional wires represent a capacitor, for operation of which an alternating current with a frequency of 500 to 5,500 Hz and a voltage of the order of 100-150 volts is needed. When charging and discharging the capacitor, under the influence of electric field, the phosphor begins to glow all along. Such a wire is better than neon tubes in all respects - it has less power consumption, it is cheaper to manufacture, it is not limited in length and can freely change its shape.

To the decorative wiring can also be attributed the one that is used for the style of "retro." These are conventional power cables, but it is assumed that they will not be hidden in the wall, but laid along its surface, with the corresponding requirements for reliability and appearance of insulation. Most often these are two or three-wire wires with strands twisted together.
These are the main cables for the transmission of electrical current, radio signals and digital data. Of course, there are still many varieties and analogues, only the enumeration of which will take a lot of time, so for the example were chosen those of them whose characteristics most fully correspond to the class of wires that they represent.
Electric wires must perform the transfer of electrical energy from source to consumer. Their tasks should be to perform these products for a long time, to be reliable, not to allow malfunctions. These products include cables and wires. They are used in almost all branches of industry and human life. Electric wires are necessary to form a closed circuit of electric current, not allowing its loss in this circuit. People who do not understand electrical engineering issues do not distinguish between different types of electrical wires, attribute all types to one category.
But this is completely wrong. Power wires are used in various operating conditions, on different highways, have many differences in application, their structure is differently structured, and they have design features. Lines electrical networks can consist on its length, both from air wires, and underground cable.
Branching of the cable on the overhead line is carried out for special purposes, which are necessary for local conditions.
Electric wires
The wire has the simplest design, which can be divided into two parts:
- A vein of metal, designed to conduct an electric current.
- Insulating layer, protecting the core from contact with foreign conductors, in order to prevent unauthorized leakage of current.
As the insulation can act and air, located around the metal core instead of a shell of dielectric materials. In this case, the wire is made bare, and the places of fixing the wires along its path on the supporting structures (poles) are made in the form of insulators (glass, ceramic).
The conductors conducting electric current are made of copper alloys and copper, as well as aluminum. The most innovative material of the conductive core is currently composite alumina. It is designed to better utilize the properties of copper and aluminum.

To perform special tasks, use cores made of steel alloys, as well as nichrome and silver. In some cases gold is used for special equipment in the veins.
Specific features of the conductor structure
The vein can be in the form:
- One-wire single-core wire having a certain length.
- Pulled out of the thinnest wires (polyhedron) operating in parallel.
Wires with one wire are much easier to make. They have a rigid shape, they are used to supply electric current with rigid attachment to the supports, have low resistance when transferring currents of low frequency, direct current.
The veins, consisting of a set of wires, have a very flexible shape, they conduct a high frequency current well.
Types of wires
Often a wire is called a product, in which one wire is made of wire. But electric wires can have several veins, twisted or doubled, with three cores and more.
Electrical cable
The cable has a more complicated design, it is designed for reliable operation under the aggressive action of negative environmental factors.
The number of conductors that conduct current is chosen according to the operating conditions. They are isolated from each other. The cable can have auxiliary elements:
- Protective braid of steel, armor of wire, or plastic.
- Filler.
- Core.
- Outdoor screen.
Each element performs its assignment functions for certain conditions.

Electricians should know the main groups, which include cables and electric wires:
- Power, acting in installations for any voltages.
- Control, transmit the data of the parameters of different systems.
- Controls are used to provide signals and commands automatically, or manually.
- Connections, to exchange signals at different frequencies.
Separate group includes special purpose cables:
- Radiating, used to feed radio signals of high frequency.
- Heating, convert electricity into heat.
Current-carrying conductors
The cores of the cables are manufactured according to the same rules as the conductors of wires, of different materials, with one conductor or multiwire, protected by a layer of insulation. According to the flexibility of the structure, the cables are divided into 7 groups. Group number 1 includes cables that are difficult to bend, have a mono. The most flexible group is number 7. The cables of this group are the most expensive.
Electric wires with multiwire flexible wires are equipped with special tips in the form of tubes (end caps) before installation. In the case of a wire, the monolithic tubes are not installed, as this makes no sense.

Shell
It performs the function of protecting the core and its insulation against damage to the environment, creates tightness from moisture and other factors, contains several layers of shielding and reinforcing elements.
The shell can consist of:
- Plastic surgery.
- Fabrics.
- Metal.
- Reinforced rubber.
Materials based on plastic are used for:
- Insulations of cores and wires with increased dielectric characteristics.
- The formation of a hose with a high tightness, which protects against damage and short circuits, with the structure of elements placed in it.
Impregnated with a special compound cable paper is used in high-voltage cables up to 35 kilovolts. Cross-linked polyethylene is used to form the insulating properties of a cable that operates in electrical devices up to 500 kilovolts with increased reliability and a long service life.
For high-voltage circuits up to 500 kilovolts, cables filled with oil were previously produced. They consisted of shielded cores installed inside a sealed cavity filled with oil. After the use of cross-linked polyethylene began, the design of oil cables became irrelevant.
Security conditions
Cable products subject to a special assessment, which includes:
- The behavior of the cable when it is closed in the channel.
- Can the cable keep long overloads.
- The behavior of the cable with open fire, the possibility of spreading fire in a fire.
- Presence of toxic substances during combustion.
Occurrence of closures
During the shorts of the veins, a high temperature is formed, which is transmitted to other cables nearby, heats them, can provoke burning. As a result, gases are generated that create an increased pressure, a breach of the air tightness of the cable channel occurs. Further, air enriched with oxygen penetrates into the channel, a fire develops.
Prolonged overloads
An electric current of large magnitude heats the metal veins and the dielectric layer of insulation together with the sheath. Chemical reactions begin that destroy the insulating layer, gases are formed that mix with air, a flame of fire is formed.
Spread Fire
The shell of plastic and some types of polyethylene can provoke combustion. This gives the possibility of a fire. A greater danger arises when the cables are positioned vertically.
According to the spread of combustion, the production of cable production is divided into:
- Ordinary.
- Not conducive to the continuation of combustion in a single gasket: horizontally and vertically.
- Not spreading the flame, from several gaskets: horizontally and vertically.
- Fireproof.
Emission of harmful substances
The cable is reacted to an external fire. Isolation can release harmful substances simply by heating, without burning. These cables can not be used in public places.
Cable Requirements
To increase reliability and safe operation, the cables are evaluated by:
- Resistance to fire.
- Resistance to insulation heating.
- The method of cutting ends.
- Protect from moisture.
Electric cord
The design of the cord is the product, the middle between the cable and insulated wire. The cord is made using special technology to create flexibility and long work.

The cord is used to create a connection between the supply network and the mobile electrical device. Household devices equipped with cords include: teapots, irons, lamps, etc.
Marking
For the sake of difference, the wires and cables are marked under the following circumstances:
- At the factory during manufacture.
- When installing.
The marking includes:
- Color marking of insulation.
- Inscriptions on the shell.
- Labels and tags.
The marking enables:
- Determine the purpose and design of the cable.
- Make the analysis of properties.
- Make an assessment of the application.
Marking during operation adds information to the available information and is produced by inscriptions and tags, which indicate the schemes and ways of laying the cable, lived between the elements. Marking can be supplemented with electronic markers. This makes it possible to determine the cable in a large number of cables.
European marking
Identification of wires by color
The insulation of the wire is colored along the entire length in one color, or colored marks are applied. The standard specifies the order in which markup is applied to specific colors.
For green and yellow colors, only their combination on the marking of one shell is allowed. It is forbidden to mark these colors separately. Such a color marking is used to refer to protected conductors.
To isolate the medium conductors, a light blue color is used. The electrical wires of the phases are marked with black, gray and brown color.
Identify the insulation of wires with letters and numbers

Such marking methods define the components of the wire and cable designs. But they do not have a complete list of information about the wires. Such information should be sought in specialized literature.
In electrical engineering, it is customary to refer to a wire as a metal conductor, which has in its structure one or more cores, through which an electric current passes. A conductor can consist of one (single-wire) or several (multiwire) copper or aluminum wires twisted together.
It should be noted that if the wire consists of several cores, then its flexibility will be much larger than a wire with a single-wire vein.
As already mentioned, the wires of wires, which are used for the manufacture of electrical installations or wiring, are made of copper or aluminum.
For the sake of economy, aluminum wires are most often used, since their cost is significantly lower compared to copper wires.
What are the wire cross sections?
The standard cross sections of copper wires are as follows: 0.5; 1; 1.5; 2.5; 4; 6; 10; 16; 25; 35; 50; 70; 95; 120; 150; 185; 240; 300; 400; 500 and 800 mm2.
Aluminum wires will have the same cross-sections, only they begin to be made with a cross section of 2.5 mm2.
If the cross-section of a copper wire does not exceed 10 mm2, then it can be either single-wire or multiwire. A similar statement is also true for aluminum wires with a cross section of not more than 25 mm2. The veins of a larger cross section will always be multiwire.
The basic design of the wires is shown in Fig. 1.
Fig. 1. : а - ПВ, АПВ; b - PPVS, ALPVS, PPPS, AFPPS; in - PPV, APPV, IFR, APPP, APPR; g.ETC , APR; e - TWP, WFD; e - LCPE; g - PRF,PRFL ; APRF; 1 - a current-carrying vein; 2 - insulation of the core; 3 - separating base; 4 - braid of cotton fabric; 5 - braid for CDD from cotton yarn, PVC for PVC; 6 - shell of PVC-plastic; 7- winding of cotton yarn; 8 - twisting of veins and winding of paper yarn; 9 - metal shell with folded seam of AMC alloy or brass
What are the wires?
Wires are classified primarily by the presence of an insulating layer - bare and insulated. In the case of an insulated wire, the conductor through which the electric current passes must be in a sheath of rubber, PVC or vinyl plastic.
In order to ensure that the wire is carefully protected from all sorts of mechanical damage or external influences, the insulation is covered with a braid of cotton material, which is pre-impregnated with an antistatic composition.
If the insulation of the wire that is laid on the vibrating mechanism or in the area where there is a risk of damage, it must have additional protection, made of a braid of galvanized steel wire.
What are the types of wires?
By marking the wire one can learn a lot about its key characteristics:
- A - bare, made of aluminum, multiwire, the cross-sectional area of the veins is in the range from 16 to 25 mm2;
- AC - bare, made of aluminum, multiwire, inside it will be a core made of galvanized wire. The cross-sectional area of the veins will be from 16 to 40 mm2;
- ACS - exactly the same wire as the speaker, only the cross-sectional area will be much larger - from 120 to 400 mm2;
- M - wire without insulation layer, made of copper. The cross-section of the current-carrying vein is 4.6 and 10 mm2. In this case, the wire will be single-wire. If it consists of several veins, its total cross-section will be 16 mm2 and even more;
- PWG - A wire with a flexible conducting vein, made of copper, the vein is placed in an insulating layer made of rubber, as an insulation can act braid of cotton yarn. The cross-section of such a wire, as a rule, is in the range from 7.5 to 25 mm2;
- DPSD - a two-wire flexible wire made of copper and placed in rubber or cotton insulation;
- PRF and APRF - the first wire is made of copper, and the second one is made of aluminum. In such wires, there may be one, two or three wires isolated from each other by rubber insulation. The entire wire is additionally wound with a rubberized cloth and covered with a metal sheath. The cross-section of wires is from 5 to 15 mm2;
- PRSP - copper wire with rubber insulation. It is wound with a rubber cloth. The number of cores can be different: 1-3, 4-10, 5-30. The cross sections will also be corresponding - 1-95; 1-10; 1-2.5 mm2;
- PRTO - a wire made of copper, placed in an insulating material, which is rubber. The outer layer of such a wire is a braid of cotton yarn, its cross-section is from 2 to 8 mm2;
- APPRW - A wire similar to the previous one, only in this case the conductor core is made of aluminum and its cross section is somewhat larger - from 4 to 12 mm2;
- PV - a copper wire with a conductive live conductor placed in an insulating layer made of polyvinyl chloride. The cross-section of such a wire is from 2 to 6 mm2;
- PPV - also a copper wire, but it has a flat shape, in itself inflexible. It can include 2-3 conductive veins, which are isolated from each other, they are further separated by a plastic material made of PVC materials;
- WSP - wire, similar to the previous one, but having the necessary flexibility;
- APAP - the same wire, only the strands are made of aluminum;
- APO - aluminum wire, placed in insulation made of PVC materials with a cross-sectional area of the wire from 2.5 to 10 mm2.
Which wires where it is better to use?
If the wires have the mark M, A, AC, ACS, then they are most suitable for manufacturing overhead lines Power transmission, the voltage in which is up to 1000 V or even slightly more.
Lay such wires on insulators, which must be fixed on the supports.
OL and APR are used in lighting and power networks, this can be done both inside and outside the premises. They are quite suitable for laying in fire-hazardous premises and in secondary circuits (for example, in insulating pipes, insulators, inside concrete or metal ceilings, with gasket for insulating materials).
PWG is used to connect various electrical machines and devices both inside and outside buildings. Such wires may be placed in metal sleeves.
PV and APV are best suited for the manufacture of lighting and power networks inside the premises. The type of premises can be any - dry, moist, especially raw, with vapors of acids or alkalis. The ambient temperature for this type of wire should not be more than 40 "C. This type of wires is used in lighting panels, launchers, as well as in enclosed cabinets designed to construct secondary circuits, for example in tubes, insulators, they can be laid on metal or concrete surfaces, only under the wires it is necessary to lay the insulating material without fail.
PGV is used for the manufacture of lighting and power circuits, for the construction of secondary circuits, they are allowed to be laid in tubes and sleeves made of metal.
PRTO, APPRTO are the most suitable for the manufacture of power and lighting networks in rooms where there is no danger of explosion. They can also be laid on the vibrating surfaces of machines, aggregates and cranes. In addition, they are used in cases where the opening of the pipeline will be problematic enough, and they are often used in secondary circuits of electrical wiring.
GTRGT, PRSP are also suitable for laying power and lighting networks, construction of secondary circuits. They are used for wiring in machines and mechanisms, even if the wire will be subjected to a mechanical impact. However, one should not allow oil or emulsions to act on such a wire.
PRF, APRF is laid in dry rooms, even if the wire will have a slight mechanical impact. These wires are used in cases where open wiring it is necessary to make imperceptible, that is, open with fastening with the help of staples. These wires are suitable for the construction of lighting and power electrical networks.
AR, ARD are laid in such rooms, where the wire does not require considerable flexibility. They are suitable for the construction of a lighting network, the voltage of which will not exceed 220 V.
DWPG can be used both inside and outside buildings, and they are also suitable for building a power grid in a damp room. The voltage in the network made of such wires should not exceed 220 V. Such wires are used where they will require a considerable degree of flexibility, for example, inside lighting fixtures.
APV, APPV are laid in dry and damp premises on walls and ceilings. These wires are able to withstand a voltage of up to 500 V. They are openly attached using nails or staples. This type of wire is suitable for lighting wiring.
APPVS are suitable for building wiring in a dry or damp room. The voltage in the network should not exceed 600 V in this case. This type of wire is suitable for hidden wiring, for its laying under a layer of plaster.
Cables and wires are an important component of the power system, from the correct choice of which depends both the repair budget and the safe operation of the electrical wiring. Therefore, those who plan to organize electricity supply, it is necessary to study every nuance - from the selection of the wire section to the features of cable laying.
Cables and wires - this is a huge range of products, which only in Russia is represented by more than 20 000 species. A wide choice of the most important part of the power systems - conductors , transmitting electric current, will make it possible to realize any ideas on electricity supply of premises. The main thing is to choose the right type of products and follow the Rules for the installation of electrical installations (PUE) when choosing the section of the core.
Remember! The correct choice of conductors is not an idle enthusiasm, but a responsible stage of repair, on which the safe operation of electrical wiring depends. Therefore, those who do not plan a close acquaintance with the terms " short circuit"," Melting insulation "or" fire ", it is recommended to stop the selection on the conductor, which corresponds to the norms of the PUE.
For a maximum current consumption and a sustained load of 25 amperes, a copper wire of 5 mm 2 cross section, corresponding to a diameter of 2.5 mm, is recommended. The minimum diameter of the conductor for the residential energy system, in accordance with the EMP, is 1.8 mm, the cross-section of the conductor is not less than 2.5 mm 2.
A wire is one uninsulated conductor or one / several isolated conductors. Depending on the presence / absence of insulation, the entire range of products is distinguished by:
- Insulated wires with insulation and braiding: cotton yarn, plastic, rubber, metal tape. Isolated, in turn, differ in two versions, depending on the presence of a protective shell:
- protected with a cladding for protection from climatic influences and hermetic sealing (brands PRVD, APRN, APRF, others);
- unprotected without the shell of the brands CD, APPRTO, APPR, PPV, APPV, others.
- Bare wires without insulating coatings. Such conductors are mainly used for overhead power lines (PS, PSO, AC, A, others).
Depending on the number of veins one- and stranded (flexible) wires, and according to the material of manufacture, the assortment is represented by three main types:
- Aluminum - Conductors made of cheap, light, chemically resistant and heat-releasing material with a decent electrical conductivity. Disadvantages - aluminum oxidizes, so there is a risk of overheating of the wire and loss of contact, and does not bend. In addition, such wires are much inferior in copper to conductivity (1.5 times).
- Copper Are flexible wires with high conductivity made of a material that does not create an oxide film. However, the products are expensive, highly dense and not "friendly" with aluminum: they form a galvanic couple on contact, which destroys the contact. Therefore, if you need to connect two kinds of conductors, you will need special terminals.

- Alumomed - a combination of an aluminum core with a copper jacket. Inexpensive mechanical composite combines the positive properties of the two predecessors, but inferior to each of the metals in terms of performance.

To create power systems, experts recommend using copper wires, as reliable in operation and not subject to corrosion material. A popular assortment of conductors - brand PPPP, PUGNP for installation of sockets and installation of lighting systems. Economy option household wires - APPPP with aluminum conductors, telephone: 1) TRP with polyethylene insulation; 2) ТРВ for installation outside; 3) flat STPP with copper cores; PRPPM increased flexibility.
A cable is one or more insulated cores twisted together, which are enclosed in a sheath (cambric): nonmetallic (plastic, rubber), metal. Depending on the operating conditions / cabling, the cable can be protected by several covers on top of the casing or stranded metal bands (armored). Additional protection from external influences is provided by fillers of various types.
The assortment of cables is classified by several features, similar to wires: according to the material of the vein, the number of conductors ... however, for experts to recommend products, experts recommend studying the marking - alphanumeric designation. On this basis, you can quickly determine the type of conductor and the main characteristics:
- core material is denoted by the first letter, while the type of the product is determined by the presence of the letter "A", since copper is not marked. Therefore, AVVG is an aluminum cable, and VVG is a copper cable;
- application area (second letter): installation - P or Y, mounting - M, control - K, installation - W, flexible mounting - MG. Absence of the second letter means a power cable;
- type of insulation (the third letter): polyvinyl chloride (B, BP), kapron (K), double winding (D), polyethylene (P), fiberglass (C), rubber (P or non-flammable HP, H), screened (E), polyamide silk (III);
- structural features (fourth letter): flexible - G, armored - B or K (round wire), braided - O, for pipes - T.
Additional information about the cable is indicated in capital letters, and the numbers consistently indicate: 1) the number of cores; 2) section. The most popular types of power cables are NYM or VVG with a PVC cambridge, as well as VVG versions: with aluminum core (AVVG), high incombustibility (BBGG), flat section (VVGP). For outdoor use it is recommended to use KG - flexible cable and its varieties.

