In our time there is no such branch of the national economy in which electricity would not be used. And each of them presents to the electric machines and apparatus certain requirements, on which not only the design of these machines depends, but also the kind of current used. Although both AC and DC are widely used in engineering and industry, the areas of their application are very clearly delineated.
For the first time people received an electric current from galvanic cells. These elements created in the electrical circuit a stream of electrons moving all the time in one definite direction. This current was called "permanent".
The first rotating generators, electric motors and instruments also worked on direct current. And when, at the end of the last century, the Russian electrical engineer MO Dolly-Dobrovolsky proposed the use of a three-phase alternating current, many scientists reacted with disbelief to this. Even the famous American electrical engineer Edison considered the alternating current to be an invention, not worthy of attention. However, very soon alternating current began to be used in many areas of electrical engineering. Electric generators of alternating current create in the electric circuit a stream of electrons, continuously changing the direction of its movement. So, in the chain of the electric bulb that illuminates your room, the electrons have time in one second
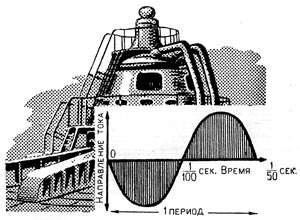
100 times to change the direction of their movement: 50 times they move in one direction and 50 - in the opposite direction. About such a current say that it has a frequency of 50 periods per second.
This feature of the motion of electrons gives an alternating current a number of properties that determined its dominant position in modern electrical engineering.
One of the most important properties of alternating current is its ability to transform. As we know, the transmission of electrical energy over long distances is possible only at very high voltages, reaching 110, 220 and even 500-800 thousand. Such a high voltage can not be obtained directly from the generators. At the same time, for various electrical machines and apparatuses, an electric current of several tens or hundreds of volts is needed. It was here that his ability to transform was useful - it allowed using transformers to change the AC voltage in any limits.
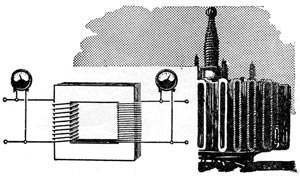
Little of. The connection of the generator windings to a three-phase system made it possible to obtain a three-phase alternating current. It is a system of three alternating currents, which have the same frequency, but differ in phase by one third of the period. Three-phase current has important advantages. First, three-phase power lines are more advantageous than single-phase ones: for them, with the same expenditure of wires and insulation, more electrical energy can be transmitted than with single-phase alternating current. And secondly, thanks to the property of three-phase alternating current to create a rotating magnetic field, it was possible to build very simple and reliable asynchronous electric motors without a collector and brushes.
These qualities of alternating current have also caused that in our days all industrial power plants produce only three-phase alternating current.
More than half of the electrical energy produced by these power plants is consumed by electric motors. So that they can perform a variety of work, they are made different in both the device and the size.
In addition to simple asynchronous motors, which are widely used to drive machines, there are motors with winding and contact rings on the rotor. They develop great efforts when starting off and are therefore successfully used on cranes. There are also synchronous motors with a constant speed of rotation. In size, electric motors are small - with a coil of thread - and huge, like a carousel.
The use of several electric motors for the drive of machine tools made it possible to simplify machine mechanisms, to facilitate the control of them and to create automatic machine lines.
The small size of electric motors allowed the use of electrical energy where manual labor had previously been used. Electric drills, saws, planes and other electrified tools have greatly facilitated the work of workers, making it more productive.
Electric floor polishers, vacuum cleaners, washing machines and refrigerators came to the aid of housewives.
![]()
Alternating current is a good source of heat. In powerful electric arc furnaces, metal is melted and brewed. Electric resistance ovens are widely used for air conditioning, heating of drying cabinets and various rooms.
Electric light bulbs give light no matter what current flows through their strands. But since AC transmission is more economical, and transformers allow easy maintenance of the voltage required for them, the entire lighting network of towns and villages is served by alternating current.
The continuous change in the direction of motion of electrons in an alternating current, and its ability to transform it, opened a wide path to him in many fields of technology. But the current is not always good, changing its direction all the time. So you boarded a trolley, a subway train, or a train car on the railway. Here you are in the possession of direct current.
The fact is that simple and convenient electric AC motors do not allow a wide variation in the speed of their rotation. And remember how many times the driver has to change the speed of the trolleybus; with such troublesome work only the DC motor can handle well. Power of these engines is carried out from traction rectifier substations. The alternating current coming to them from power stations with the help of mercury rectifiers is converted into a permanent one, and then fed into a contact network - into wires and rails.
The use of DC traction motors on transport vehicles has proved so beneficial that they can be found on locomotives and motor ships.
Their main engines are diesel engines, which drive generators that produce direct current. And it, in turn, forces electric motors, rotating wheels or propellers to work.
However, the high cost and complexity of the converter substations made scientists and engineers think about the use of alternating current in transport. Now there are sections of railways using single-phase alternating current. With success, it is used on many diesel-electric ships.
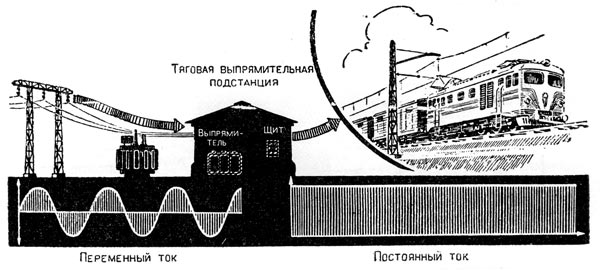
Further electrification of railways in our country will be carried out mainly with the use of an alternating current of 25 thousand volts. This current will be converted into a constant directly on electric locomotives by means of rectifying devices.
Good adjusting ability of DC motors allowed to successfully apply them also on hoisting and transport mechanisms. On conventional cranes, which you see on the construction, AC motors operate. But on powerful cranes of large metallurgical plants, DC motors are installed. After all, you need to smoothly lift and carry huge buckets with molten metal, pour it into molds or serve hot pellets at rolling mills.
These engines set in motion the mechanisms of giant walking excavators.
DC motors can develop very high rotational speeds - up to 25 thousand rpm. This allows you to get more power with a very small engine size. Therefore, they are indispensable as the control motors used on aircraft to rotate rudders, ailerons and flaps, for lifting and lowering the chassis and other mechanisms.
The invariable direction of the motion of electrons in the DC circuit has determined a large and important area of its application, in which an alternating current with it can not compete. We are talking about electrolysis - a process associated with the passage of current through liquid solutions - electrolytes. Under the influence of a direct current passing through the electrolyte, it decomposes into separate elements, which are deposited on certain electrodes - on the anode or cathode. This property is widely used in non-ferrous metallurgy - for the production of aluminum, magnesium, zinc, copper, manganese. In the chemical industry, electrolysis produces fluorine, chlorine, hydrogen and other substances.
In electroplating, electrolysis is used to deposit metal on the surface of various products. Thus, protective coatings are applied to metal products (nickel plating, chromium plating), metal monuments, printing forms, etc. are manufactured. Galvanization is used in medicine for the treatment of certain diseases.
The constant direction of the motion of the electrons helps the DC to compete with the variable in the welding process and some types of lighting. When welding with direct current, metal particles are transferred from the electrode to the product more correctly and the weld is obtained more qualitatively than when welding with alternating current.
Go to the film studio. Powerful arc projectors flood the light with a shooting pavilion. At alternating current, the arc burns less steadily, gives less light and produces a buzz that interferes with the recording of sound during filming. Therefore, the film projectors supply a constant current, which gives a noiseless stable arc. In powerful military searchlights and arc cinema projection devices, direct current is also used.
![]()
In order to obtain an alternating current, it is necessary to continuously rotate the alternator, and a constant current can produce stationary batteries or galvanic cells. These properties of the source of electric current also in a number of cases determine the area of application of direct current.
The car stands still. How to start his engine? You have a rechargeable battery. You press the starter button, and the DC motor, getting power from the battery, starts the motor. And when the motor is running, it rotates the generator, which charges the battery, restores the energy expended. Such a reversible process is not available for alternating current.
What would have happened if the lighting was powered by alternating current in trains? The train stopped - the wheels of the cars stopped spinning, and with it electric generators would stop and the light in the cars would go out. But this does not happen, because under the cars there are direct current generators working in parallel with the batteries. There is a train - the generators rotate, give energy for lighting and simultaneously charge the battery. The composition stopped - the battery sends a current to the lighting network.
Imagine that an accident occurred at the power plant: all turbo or hydro generators stopped and the power lines that connected it to other power stations were turned off. In such cases, the direct current produced by the large batteries will help. With its help, auxiliary mechanisms are activated, switches are turned off and the main turbo or hydrogenerators are re-commissioned. The battery power supply is very reliable, therefore all control, automation and alarm control circuits in large power plants operate at DC.
Can a submarine float without a direct current? On the surface of the water can. In this case, its propellers rotate with diesels. But under water, diesel engines stop - there is not enough air. There is a DC motor, which receives energy from the batteries. When the boat re-emerges to the surface and the diesels start working, the electric motor turns into a generator and recharges the batteries.
In mines, it is not always possible to hang a contact wire for electric locomotives. How can they move around? And then the battery recharges again. At many mines, mine battery electric locomotives deliver coal from the most remote faces. Electric carts with batteries - electric cars - you often see at the train stations. They are also in the shops of large factories and factories.
Notice how the cameraman removes an important event. In his hands he has a light film camera, and on the belt - a battery. I pressed the button and the device started working. Such lightweight batteries are widely used for portable radios, signaling devices, electrical measuring instruments.
Of course, the examples listed here do not exhaust all fields of application of electrical energy. We did not tell you anything about its use for telegraph and telephone communication, for radio and television and other purposes - you will read about it in the relevant articles of our website.
5.1. WHY THE AC VOLTAGE IS NEEDED?
In the first electrotechnical installations only direct current was used. However, it soon became clear that it is much more advantageous to use not a constant but an alternating current, that is, one that periodically changes its meaning and direction.
First of all, alternating current is more convenient to produce at power plants. AC generators are simpler and cheaper than analogous DC generators.
It was also found out that it is more advantageous to transmit electric current through wires at high voltage. To change the AC voltage is very simple - you need to use a transformer for this. On DC, this is much more difficult.
Simple and reliable AC electric motors have been designed that are very widely used in industry.
But all these are such applications where an alternating current can compete with a constant one. Generators, transmission lines and electric motors can be executed both on a constant and on an alternating current. However, there are such physical phenomena that manifest themselves only when the current changes.
These phenomena are widely used in radio engineering, automatics, electronics, and so on.
We can say that if there was no alternating current, there would not be many of these branches of electrical engineering.
In radio receivers, televisions, tape recorders, use alternating currents and replace them with constant current is impossible in principle.
Many technological processes in industry are also based on alternating current.
Instructions
First let's see what is an electric current. A directed motion (flow) of charged particles is called an electric current. In an alternating electric current, a different number of charged particles pass through the cross section of the conductor at equivalent time intervals. In the same constant, the number of given particles at identical intervals of time is always the same.
The alternating current constantly changes its strength, magnitude or direction. And these changes occur periodically, that is, they are repeated at regular intervals. For example, using a variable current It is impossible to charge the battery or you can not use it for such technical purposes.
Unlike the permanent current, the variable has several additional values: - period - the time value of the completion of a complete cycle of indicators of the variable current; half-cycle and frequency (number of cycles per specific time interval) - amplitude - the highest value of the variable current- instantaneous value - value current at a given time.
Alternating current is more common and widely used. It is easier to convert into an alternating current of another voltage, change the voltage in the electrical networks depending on the needs. This can be done with a transformer. Transformer is an apparatus that converts an alternating current of one voltage into the same current, but of a different voltage at the same frequency current.
Croupous pneumonia begins acutely, most often, after severe hypothermia. The temperature rises sharply to 39-40 degrees, the patient beats a strong chill. Immediately there is pain when breathing and coughing from the side of the affected lung. Cough is accompanied by the release of purulent viscous sputum with blood veins. The patient's condition is difficult. Breathing shallow, rapid, swelling of the wings of the nose. The affected side of the chest is markedly lagging behind when breathing from a healthy one.
On planet Earth to date, 98% of all electricity is generated by alternating current generators. Such a current is easy enough to produce and transmit over long distances. In this case, the current and voltage can repeatedly increase and decrease - transform. The work is done not by voltage, but by current. Therefore, the lower its value, the less the loss in the wires.
Many users believe that at home only AC is used with a voltage of 220V and a frequency of 50Hz. This is only true for incandescent lamps, electric motors in vacuum cleaners, refrigerators.
In any complex household device powered by an alternating current network, there are nodes that operate at a constant voltage with different values. To foresee what these values may be, it is virtually impossible. Therefore, all consumers in the outlet have alternating current of the same frequency and voltage.
D.C
Despite the fact that the share of DC output is only 2%, its value is quite large. Constant current is produced by galvanic cells, batteries, thermocouples, solar batteries.
Solar panels are becoming a very promising direction of energy in today's days, when the issue of using renewable energy sources is sharply raised.
The direct current feeds the locomotive engines on the railway transport, it is used in the onboard network of aircraft and automobiles.
On the roads of modern cities is becoming more electric vehicles and hybrid cars. To recharge their batteries, stations are built, which ensure their needs for constant current.
What should be the sockets
The dimensions of the sockets, their type, the material from which they are made depend primarily on the purpose of the sockets, currents and voltages to which they are designed. Devices operating under constant voltage have polarized plugs. Therefore, the sockets for them must be polar. Then even an inexperienced user can not mix up where "+" and "-" are.
The alternating current in the circuit is the electric flow of charged particles, the direction and velocity of which periodically varies with time according to a certain law.
Instructions
Refer to the general concept of alternating current in the electrical circuit described in the school textbook. There you will see that an alternating current is an electric current whose value varies according to a sinusoidal or cosine law. This means that the magnitude of the current in the AC network varies according to the law of the sine or cosine. Strictly speaking, this corresponds to the current that flows in the household electrical network. However, the sinusoidal current is not a general definition of alternating current and does not fully explain the nature of its flow.
Draw a graph of the sinusoid on a sheet of paper. This graph shows that the value of the function expressed by the current strength in this context changes from positive to negative. And the time, through which the sign changes, is always the same. This time is called the period of current oscillations, and the time inverse is called the frequency of the alternating current. For example, the frequency of the AC household current is 50 Hz.
Pay attention to what it means to change the sign of the function physically. In fact, this only means that at some point in time the current begins to flow in the opposite direction. And, if the law of change is sinusoidal, then the change in the direction of motion does not occur abruptly, but with gradual inhibition. Hence the concept of alternating current, and the main difference between it and the constant, which always flows in the same direction and has a constant value. As is known, the direction of the current is given by the direction of positively charged particles in the circuit. Thus, in a circuit of alternating current, charged particles after a certain time change the direction of their movement to the opposite.
